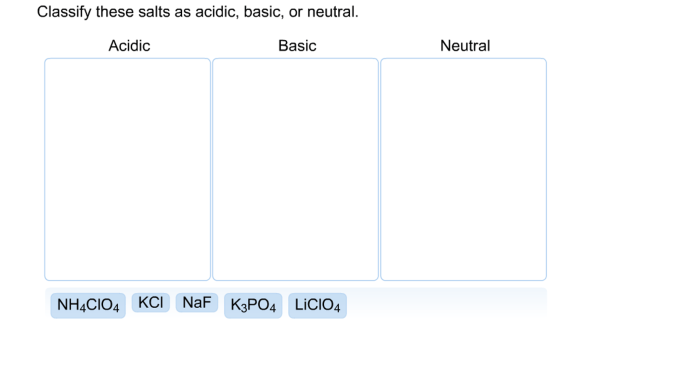
Classify these salts as acidic basic neutral – As we embark on the classification of salts as acidic, basic, or neutral, we delve into a captivating exploration of pH and its significance in determining the acidity or basicity of solutions. Salts, formed from the harmonious union of acids and bases, present a fascinating array of properties and applications.
Through a comprehensive table, we will dissect the composition of various salts, unveiling their acidic, basic, or neutral nature based on their acid and base sources. This understanding will empower us to predict the chemical behavior of these salts and harness their unique properties for diverse applications.
Classification of Salts: Classify These Salts As Acidic Basic Neutral
Salts are ionic compounds formed when an acid reacts with a base. The resulting salt contains the positively charged ions (cations) from the base and the negatively charged ions (anions) from the acid. Salts can be classified as acidic, basic, or neutral based on their pH when dissolved in water.
The pH of a solution is a measure of its acidity or basicity. A pH of 7 is neutral, a pH less than 7 is acidic, and a pH greater than 7 is basic. The pH of a salt solution depends on the strength of the acid and base that formed the salt.
Acidic salts are formed when a strong acid reacts with a weak base. The resulting salt contains a weak base cation and a strong acid anion. When dissolved in water, the weak base cation hydrolyzes to form hydroxide ions (OH-), which increases the pH of the solution.
Examples of acidic salts include ammonium chloride (NH 4Cl) and sodium hydrogen sulfate (NaHSO 4).
Basic salts are formed when a weak acid reacts with a strong base. The resulting salt contains a weak acid anion and a strong base cation. When dissolved in water, the weak acid anion hydrolyzes to form hydrogen ions (H+), which decreases the pH of the solution.
Examples of basic salts include sodium acetate (CH 3COONa) and potassium carbonate (K 2CO 3).
Neutral salts are formed when a strong acid reacts with a strong base. The resulting salt contains a strong acid anion and a strong base cation. When dissolved in water, neither the anion nor the cation hydrolyzes, so the pH of the solution remains neutral.
Examples of neutral salts include sodium chloride (NaCl) and potassium nitrate (KNO 3).
FAQ Insights
What is the difference between an acidic salt and a basic salt?
Acidic salts are formed from a strong acid and a weak base, while basic salts are formed from a weak acid and a strong base.
How can I determine the pH of a salt solution?
The pH of a salt solution can be determined using a pH meter or by calculating it based on the dissociation constant of the salt.
What are some common applications of salts?
Salts have a wide range of applications, including food preservation, medicine, detergents, cleaning products, fertilizers, and water softeners.