Dna rna and protein synthesis study guide answer key – Welcome to the DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis Study Guide Answer Key, your comprehensive resource for understanding the fundamental processes that govern life. This guide delves into the intricate structures and functions of DNA and RNA, exploring their roles in protein synthesis and gene regulation.
Through a captivating journey of scientific discovery, we will uncover the secrets of genetic information and its profound impact on our existence.
DNA Structure and Function
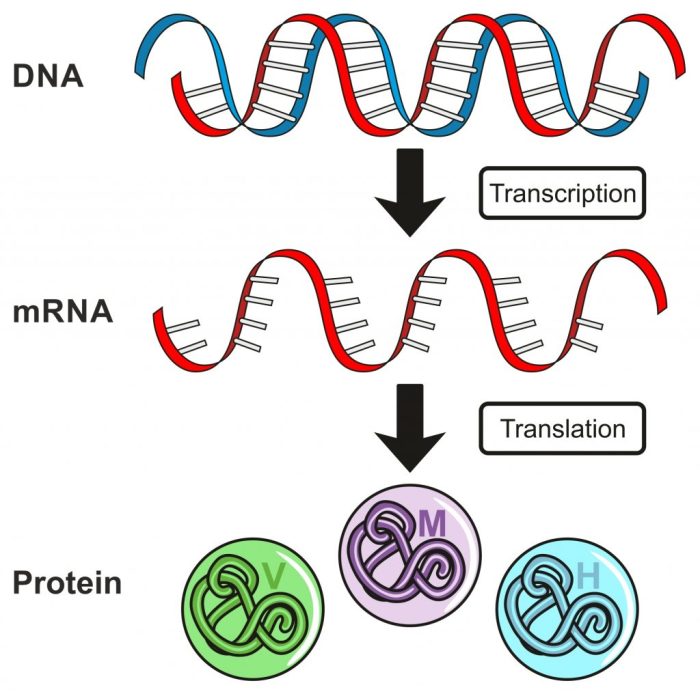
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a molecule that contains the instructions for an organism’s development and characteristics. It is found in the nucleus of cells and is made up of two long chains of nucleotides.
Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule, a phosphate molecule, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). The sequence of these bases along the DNA chain determines the genetic code.
DNA is essential for life. It stores the genetic information that is passed on from parents to offspring. It also plays a role in protein synthesis, which is the process by which cells make proteins.
Role of DNA in Genetic Engineering and DNA Fingerprinting
- Genetic engineering is a process by which the DNA of an organism is altered to change its traits. This can be done to improve crop yields, create new medicines, or treat diseases.
- DNA fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals by comparing their DNA profiles. This technique is used in forensic science, paternity testing, and other applications.
RNA Structure and Function
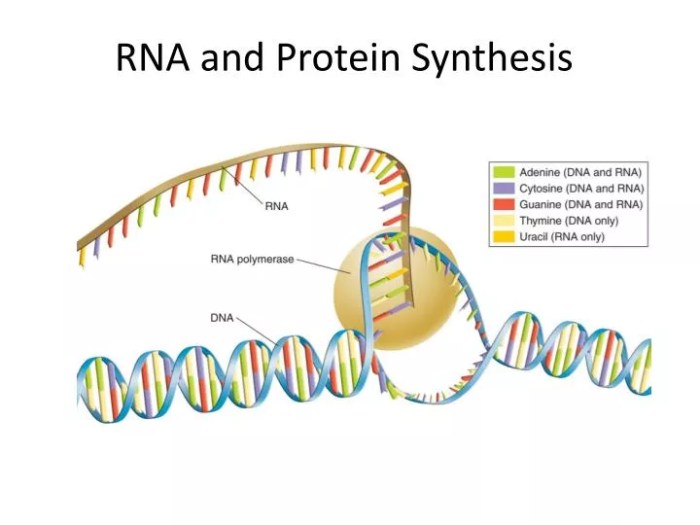
RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a molecule that is similar to DNA but has a different structure and function. RNA is made up of a single chain of nucleotides, and the nitrogenous base uracil (U) replaces thymine (T).
There are several different types of RNA molecules, each with a specific function. The main types of RNA are:
- Messenger RNA (mRNA)carries the genetic code from DNA to the ribosomes, where proteins are made.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA)brings amino acids to the ribosomes in the correct order, as specified by the mRNA.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)is a component of the ribosomes and helps to catalyze the formation of peptide bonds.
RNA is essential for protein synthesis. It also plays a role in gene regulation and RNA interference.
Role of RNA in Gene Regulation and RNA Interference, Dna rna and protein synthesis study guide answer key
- Gene regulation is the process by which cells control the expression of genes. RNA molecules can play a role in gene regulation by binding to DNA and preventing it from being transcribed.
- RNA interference is a process by which cells can silence genes by degrading mRNA molecules.
Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells make proteins. This process occurs in two stages:
- Transcription: In transcription, the DNA sequence of a gene is copied into a complementary mRNA molecule.
- Translation: In translation, the mRNA molecule is used as a template to synthesize a protein. This process occurs on the ribosomes.
Protein synthesis is essential for life. Proteins are used for a variety of purposes, including:
- Structural support
- Enzyme catalysis
- Hormone signaling
- Immune response
Mutations in protein-coding genes can lead to diseases. These diseases can be caused by changes in the structure or function of the protein.
Gene Expression and Regulation: Dna Rna And Protein Synthesis Study Guide Answer Key

Gene expression is the process by which the information in genes is used to produce proteins. This process is regulated by a variety of factors, including:
- Transcription factors: These proteins bind to DNA and control the transcription of genes.
- Enhancers: These DNA sequences increase the transcription of genes.
- Silencers: These DNA sequences decrease the transcription of genes.
Gene regulation is essential for development, differentiation, and disease.
Mechanisms of Gene Regulation
- Transcriptional control: This type of gene regulation occurs at the level of transcription. Transcription factors bind to DNA and either promote or inhibit the transcription of genes.
- Post-transcriptional control: This type of gene regulation occurs after transcription but before translation. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small RNA molecules that can bind to mRNA molecules and prevent them from being translated.
- Translational control: This type of gene regulation occurs at the level of translation. Proteins can bind to mRNA molecules and prevent them from being translated.
User Queries
What is the structure of DNA?
DNA consists of a double helix formed by two antiparallel strands of nucleotides, each composed of a nitrogenous base, a sugar molecule, and a phosphate group.
How does RNA differ from DNA?
RNA is a single-stranded molecule that contains the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose and the nitrogenous base uracil instead of thymine.
What is the role of ribosomes in protein synthesis?
Ribosomes are cellular structures that facilitate the translation of mRNA into proteins by reading the genetic code and assembling amino acids in the correct sequence.
