Do i have gum disease quiz – Do you ever wonder if you might have gum disease? This quiz will help you assess your risk and learn more about the signs and symptoms of this common condition.
Gum disease is a serious infection that can damage the gums and bone that support your teeth. It’s caused by bacteria that build up on the teeth and gums, and if left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss.
Signs and Symptoms
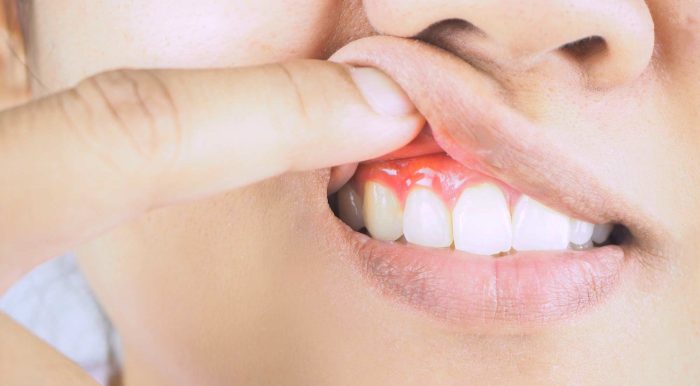
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that affects the gums and the bones supporting the teeth. It’s caused by bacteria that form plaque on the teeth, which can lead to inflammation and damage to the gums and bone.
Gum disease can range from mild to severe, and it can affect people of all ages. The early stages of gum disease, known as gingivitis, are often reversible with good oral hygiene. However, if left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, which can cause permanent damage to the gums and bone.
Redness and Swelling
One of the most common signs of gum disease is redness and swelling of the gums. Healthy gums are typically pink and firm, but gums that are affected by gum disease may become red, swollen, and tender.
If you’re wondering “do I have gum disease?”, you’re not alone. Millions of people around the world suffer from gum disease, and it’s important to catch it early for effective treatment. One way to learn more about gum disease is to check out resources like phases of matter bill nye . This site offers a comprehensive overview of the disease, including symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
After understanding gum disease, don’t forget to consult a dentist for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Redness and swelling of the gums can be caused by inflammation, which is the body’s response to infection. When the gums are inflamed, they become more sensitive and prone to bleeding.
Bleeding
Bleeding gums are another common sign of gum disease. Healthy gums do not bleed when brushed or flossed, but gums that are affected by gum disease may bleed easily.
Bleeding gums can be caused by inflammation and damage to the blood vessels in the gums. When the gums are inflamed, the blood vessels become more fragile and prone to bleeding.
Pain
Pain is a less common sign of gum disease, but it can occur in more advanced stages of the disease. Pain can be caused by inflammation and damage to the gums and bone.
Pain from gum disease can range from mild to severe, and it can be constant or intermittent. In some cases, pain from gum disease can be severe enough to interfere with eating and sleeping.
Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Gum disease is a serious condition that can lead to permanent damage to the gums and bone. However, it is often preventable and reversible in the early stages.
Early detection and treatment of gum disease is essential to prevent further damage and to maintain a healthy smile. If you have any of the signs or symptoms of gum disease, it is important to see your dentist for a diagnosis and treatment.
Risk Factors

Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that affects the gums and the structures supporting the teeth. It is caused by a bacterial infection that triggers inflammation in the gums. While poor oral hygiene is the primary cause of gum disease, several other factors can increase the risk of developing it.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Inadequate oral hygiene is the most significant risk factor for gum disease. When plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, accumulates on the teeth, it can irritate the gums and cause inflammation. If plaque is not removed regularly through brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, which further irritates the gums and makes them more susceptible to infection.
Smoking
Smoking is another major risk factor for gum disease. Chemicals in tobacco smoke damage the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off bacterial infections. Smoking also reduces blood flow to the gums, which can lead to gum recession and bone loss.
Diabetes
People with diabetes are more likely to develop gum disease because high blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system and make the gums more susceptible to infection. Additionally, diabetes can reduce blood flow to the gums, which can also contribute to gum disease.
Genetics
Some people are more genetically predisposed to developing gum disease than others. Certain genes can affect the body’s immune response to bacteria in the mouth, making some individuals more likely to develop gum disease even with good oral hygiene.
Lifestyle Choices and Habits
Certain lifestyle choices and habits can also increase the risk of developing gum disease. These include:
- Poor nutrition: A diet low in vitamins and minerals can weaken the immune system and make the gums more susceptible to infection.
- Stress: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of gum disease.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as steroids and immunosuppressants, can suppress the immune system and increase the risk of gum disease.
- Age: The risk of gum disease increases with age. This is because the gums naturally recede as we get older, exposing more of the tooth root to bacteria.
By understanding the risk factors for gum disease and making lifestyle changes to reduce your risk, you can help prevent or manage this common condition.
Diagnosis and Treatment
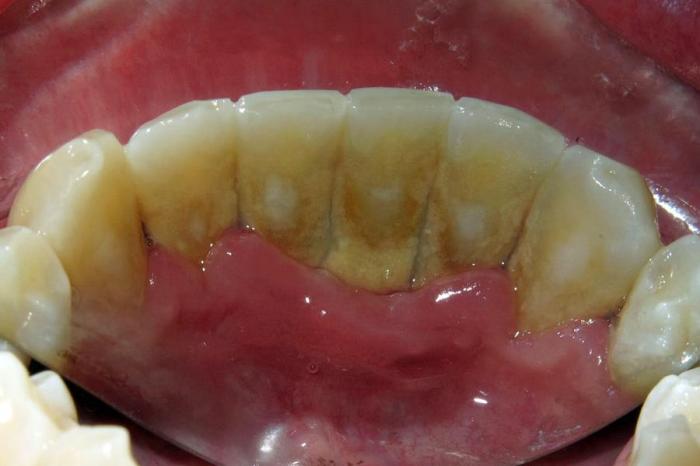
Gum disease can be diagnosed through a combination of visual exams, periodontal probing, and X-rays. During a visual exam, the dentist will check for signs of inflammation, bleeding, and gum recession. Periodontal probing involves gently inserting a probe into the space between the tooth and gum to measure the depth of the periodontal pocket.
X-rays can reveal any underlying bone loss or other structural changes.
Treatment Options
Treatment for gum disease depends on the severity of the condition. In the early stages, scaling and root planing may be sufficient. This involves removing plaque and tartar from the teeth and smoothing the root surfaces to discourage bacterial growth.
Antibiotics may also be prescribed to treat any underlying infection.
In more advanced cases, surgery may be necessary. This may involve removing diseased tissue, repairing damaged bone, or grafting new tissue to restore the health of the gums. Regular dental checkups and professional cleanings are essential for preventing and treating gum disease.
They allow the dentist to monitor the condition of the gums and teeth, and to provide early intervention if necessary.
Prevention and Home Care
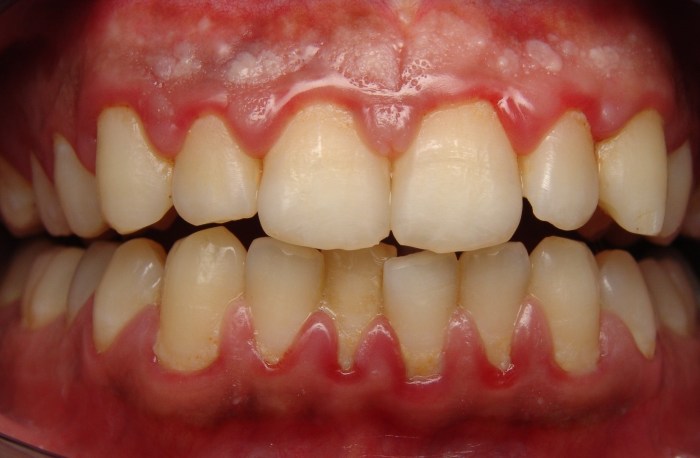
Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial for preventing gum disease. Simple yet effective daily habits can help you keep your gums healthy and prevent the onset of this condition.
Brushing and Flossing, Do i have gum disease quiz
Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Brush for at least two minutes, gently massaging the gums while brushing. Flossing is equally important as it removes plaque and food particles from between teeth, where brushing cannot reach.
Mouthwash and Other Products
Mouthwash can help reduce bacteria in the mouth and freshen breath. Choose a mouthwash that contains fluoride to strengthen tooth enamel and prevent cavities. Other oral care products like tongue scrapers and interdental brushes can also help remove plaque and bacteria from hard-to-reach areas.
Regular Dental Checkups and Cleanings
Regular dental checkups and professional cleanings are essential for early detection and treatment of gum disease. During these appointments, your dentist will examine your teeth and gums, remove plaque and tartar, and provide personalized advice on maintaining good oral hygiene.
FAQ Overview: Do I Have Gum Disease Quiz
What are the signs and symptoms of gum disease?
The signs and symptoms of gum disease include:
- Red, swollen, or bleeding gums
- Gums that are receding from the teeth
- Pus between the teeth and gums
- Loose teeth
- Pain when chewing
What are the risk factors for gum disease?
The risk factors for gum disease include:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Genetics
- Certain medications
How is gum disease treated?
Gum disease is treated with a variety of methods, depending on the severity of the disease. Treatment may include:
- Scaling and root planing
- Antibiotics
- Surgery
Can gum disease be prevented?
Gum disease can be prevented by practicing good oral hygiene, which includes:
- Brushing your teeth twice a day
- Flossing your teeth once a day
- Eating a healthy diet
- Avoiding tobacco products
- Seeing your dentist for regular checkups and cleanings